Cloud concepts have existed for many years. Traditionally, to set up an app, you would compile some hardware and software components, and as the number of visitors to your site expanded, you purchased more resources, which required more management.
Cloud computing has grown through several phases, including Grid Computing, Utility Computing, Application Service Provision, and Software as a Service, with the underlying concept of moving these components (storage, compute resources, etc) to the Internet.
According to Microsoft Azure, we can define cloud computing as the delivery of computing services like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence - over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
Benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing offers many benefits. Here are some common reasons organizations are turning to cloud computing services:
Cost: Organizations don’t have to spend a massive amount of money to buy hardware. Cloud computing also cuts costs related to downtime.
Pay-per-use: Users get to pay for only the resources and workload that they use.
Broad Network Access: Authorized users can get or upload data to the cloud from anywhere with an internet connection, using any device.
Multi-tenancy: Many customers share the same physical infrastructure, yet they still have privacy and security over their data.
Resource pooling: Allows customers to share the same physical resources.
Reliability: Cloud computing allows data backup and disaster recovery. Also, data can be at multiple redundant sites on the cloud provider’s network.
Types of cloud computing
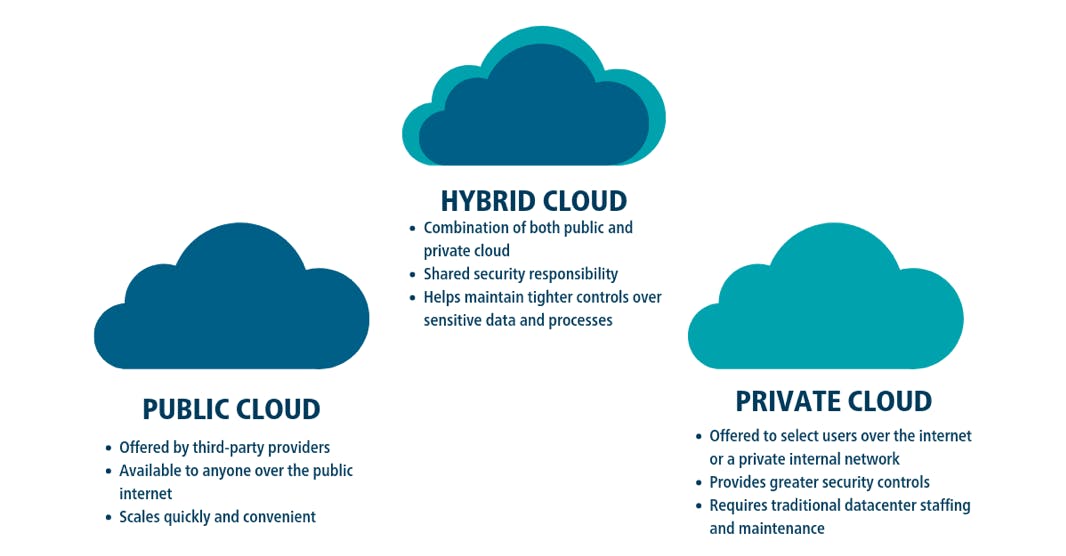
First, you need to determine the cloud computing architecture that you will implement. There are three distinct ways to deploy cloud services: on a public cloud, private cloud, or hybrid cloud. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, and which one you choose will depend on your data and the level of security and management you need:
Public Cloud: Public cloud providers, like Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure, to name a few, deliver computing resources like servers and storage over the Internet. All hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider. You access these services and manage your account using a web browser.
Private Cloud: With private clouds, computing resources are governed, owned, and operated by a single organization. A private cloud is one in which we maintain the services and infrastructure on a private network.
Hybrid Cloud: This is the combination of public cloud and private cloud. A hybrid cloud gives your business greater flexibility, more deployment options, and helps optimize your existing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
Types of Cloud Services
Cloud services come in three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- IaaS: IaaS provides access to computing resources in a virtualized environment (“the cloud”) on the Internet. It provides computing infrastructure like virtual server space, network connections, bandwidth, load balancers, and IP addresses. The pool of hardware resources is extracted from multiple servers and networks usually distributed across many data centers. This provides redundancy and reliability to IaaS.
Popular IaaS cloud providers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Compute Engine (GCE), the IaaS component of Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
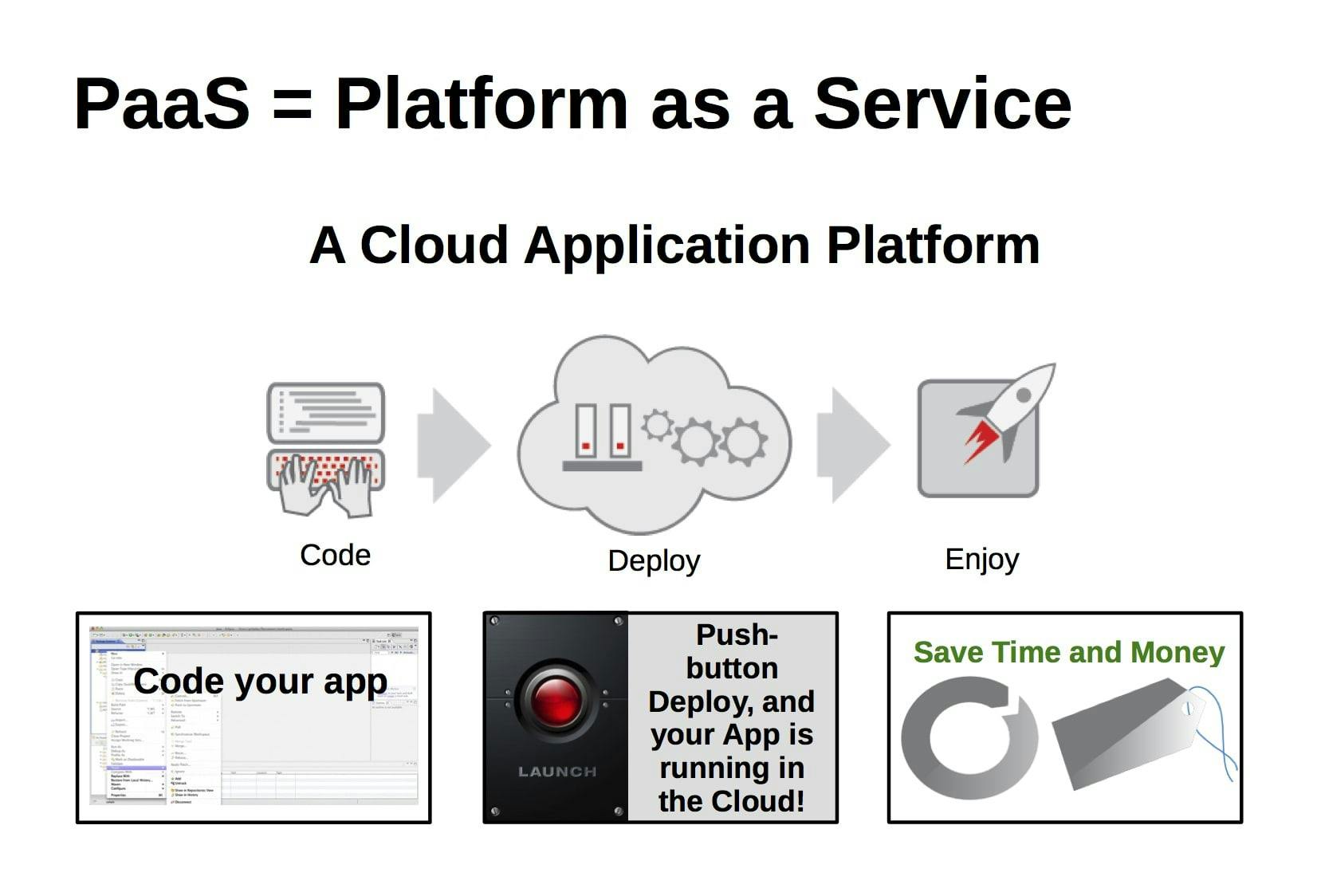
- PaaS: It provides a platform and environment to allow developers to build applications and services. This service is hosted in the cloud and users access these tools over the Internet using APIs, web portals, or gateway software. It includes software support and management services, storage, networking, deployment, testing, collaboration, hosting, and maintenance of applications. Heroku is a good example of a PaaS cloud provider.
- SaaS: It delivers software applications over the Internet; these applications are often called web services. With SaaS, cloud providers host and manage the software application and underlying infrastructure and handle any maintenance, like software upgrades and security patching. An example of a SaaS application is Microsoft Office 365 for productivity and email services.
Cloud enabling innovation
To remain competitive, cloud providers are constantly expanding their services to further differentiate their solutions. As a result, cloud providers are often able to offer far more in the way of usability, reliability, and scalability than traditional compute and storage instances.
For example, serverless, or event-driven computing is a cloud service that executes specific functions, such as image processing and database updates.
With serverless computing, developers create code, and the cloud provider loads and executes that code in response to real-world events, so users don’t have to worry about the server or instance aspect of the cloud deployment.
Resources
Cloud Computing Wikipedia